Topological space
Topological spaces are mathematical structures that allow the formal definition of concepts such as convergence, connectedness, and continuity. They appear in virtually every branch of modern mathematics and are a central unifying notion. The branch of mathematics that studies topological spaces in their own right is called topology.
Definition
A topological space is a set X together with  , a collection of subsets of X, satisfying the following axioms:[1]
, a collection of subsets of X, satisfying the following axioms:[1]
- The empty set and X are in
 .
.  is closed under arbitrary union.
is closed under arbitrary union. is closed under finite intersection.
is closed under finite intersection.
The collection  is called a topology on X. The elements of X are usually called points, though they can be any mathematical objects. A topological space in which the points are functions is called a function space. The sets in
is called a topology on X. The elements of X are usually called points, though they can be any mathematical objects. A topological space in which the points are functions is called a function space. The sets in  are called the open sets, and their complements in X are called closed sets. A subset of X may be neither closed nor open, either closed or open, or both. A set that is both closed and open is called a clopen set.
are called the open sets, and their complements in X are called closed sets. A subset of X may be neither closed nor open, either closed or open, or both. A set that is both closed and open is called a clopen set.
Examples
 = {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection
= {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection  = {{ }, {1, 2, 3, 4}} of only the two subsets of
= {{ }, {1, 2, 3, 4}} of only the two subsets of  required by the axioms form a topology, the trivial topology (indiscrete topology).
required by the axioms form a topology, the trivial topology (indiscrete topology). = {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection
= {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection  = {{ }, {2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 3, 4}} of six subsets of
= {{ }, {2}, {1, 2}, {2, 3}, {1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 3, 4}} of six subsets of  form another topology.
form another topology. = {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection
= {1, 2, 3, 4} and collection  =
= 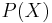 (the power set of
(the power set of  ) form a third topology, the discrete topology.
) form a third topology, the discrete topology. =
= 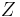 , the set of integers, and collection
, the set of integers, and collection  equal to all finite subsets of the integers plus
equal to all finite subsets of the integers plus 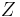 itself is not a topology, because (for example) the union of all finite sets not containing zero is infinite but is not all of
itself is not a topology, because (for example) the union of all finite sets not containing zero is infinite but is not all of 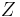 , and so is not in
, and so is not in  .
.
Equivalent definitions
There are many other equivalent ways to define a topological space. (In other words, each of the following defines a category equivalent to the category of topological spaces above.) For example, using de Morgan's laws, the axioms defining open sets above become axioms defining closed sets:
- The empty set and X are closed.
- The intersection of any collection of closed sets is also closed.
- The union of any pair of closed sets is also closed.
Using these axioms, another way to define a topological space is as a set X together with a collection  of subsets of X satisfying the following axioms:
of subsets of X satisfying the following axioms:
- The empty set and X are in
 .
. - The intersection of any collection of sets in
 is also in
is also in  .
. - The union of any pair of sets in
 is also in
is also in  .
.
Under this definition, the sets in the topology  are the closed sets, and their complements in X are the open sets.
are the closed sets, and their complements in X are the open sets.
Another way to define a topological space is by using the Kuratowski closure axioms, which define the closed sets as the fixed points of an operator on the power set of X.
A neighbourhood of a point x is any set that has an open subset containing x. The neighbourhood system at x consists of all neighbourhoods of x. A topology can be determined by a set of axioms concerning all neighbourhood systems.
A net is a generalisation of the concept of sequence. A topology is completely determined if for every net in X the set of its accumulation points is specified.
Comparison of topologies
A variety of topologies can be placed on a set to form a topological space. When every set in a topology 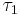 is also in a topology
is also in a topology 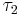 , we say that
, we say that 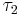 is finer than
is finer than 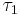 , and
, and 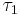 is coarser than
is coarser than 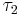 . A proof that relies only on the existence of certain open sets will also hold for any finer topology, and similarly a proof that relies only on certain sets not being open applies to any coarser topology. The terms larger and smaller are sometimes used in place of finer and coarser, respectively. The terms stronger and weaker are also used in the literature, but with little agreement on the meaning, so one should always be sure of an author's convention when reading.
. A proof that relies only on the existence of certain open sets will also hold for any finer topology, and similarly a proof that relies only on certain sets not being open applies to any coarser topology. The terms larger and smaller are sometimes used in place of finer and coarser, respectively. The terms stronger and weaker are also used in the literature, but with little agreement on the meaning, so one should always be sure of an author's convention when reading.
The collection of all topologies on a given fixed set X forms a complete lattice: if F = {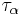 :
: 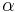 in A} is a collection of topologies on X, then the meet of F is the intersection of F, and the join of F is the meet of the collection of all topologies on X that contain every member of F.
in A} is a collection of topologies on X, then the meet of F is the intersection of F, and the join of F is the meet of the collection of all topologies on X that contain every member of F.
Continuous functions
A function between topological spaces is called continuous if the inverse image of every open set is open.[2] This is an attempt to capture the intuition that there are no "breaks" or "separations" in the function. A homeomorphism is a bijection that is continuous and whose inverse is also continuous. Two spaces are called homeomorphic if there exists a homeomorphism between them. From the standpoint of topology, homeomorphic spaces are essentially identical.
In category theory, Top, the category of topological spaces with topological spaces as objects and continuous functions as morphisms is one of the fundamental categories in mathematics. The attempt to classify the objects of this category (up to homeomorphism) by invariants has motivated and generated entire areas of research, such as homotopy theory, homology theory, and K-theory, to name just a few.
Examples of topological spaces
A given set may have many different topologies. If a set is given a different topology, it is viewed as a different topological space. Any set can be given the discrete topology in which every subset is open. The only convergent sequences or nets in this topology are those that are eventually constant. Also, any set can be given the trivial topology (also called the indiscrete topology), in which only the empty set and the whole space are open. Every sequence and net in this topology converges to every point of the space. This example shows that in general topological spaces, limits of sequences need not be unique. However, often topological spaces must be Hausdorff spaces where limit points are unique.
There are many ways of defining a topology on R, the set of real numbers. The standard topology on R is generated by the open intervals. The set of all open intervals forms a base or basis for the topology, meaning that every open set is a union of some collection of sets from the base. In particular, this means that a set is open if there exists an open interval of non zero radius about every point in the set. More generally, the Euclidean spaces Rn can be given a topology. In the usual topology on Rn the basic open sets are the open balls. Similarly, C and Cn have a standard topology in which the basic open sets are open balls.
Every metric space can be given a metric topology, in which the basic open sets are open balls defined by the metric. This is the standard topology on any normed vector space. On a finite-dimensional vector space this topology is the same for all norms.
Many sets of linear operators in functional analysis are endowed with topologies that are defined by specifying when a particular sequence of functions converges to the zero function.
Any local field has a topology native to it, and this can be extended to vector spaces over that field.
Every manifold has a natural topology since it is locally Euclidean. Similarly, every simplex and every simplicial complex inherits a natural topology from Rn.
The Zariski topology is defined algebraically on the spectrum of a ring or an algebraic variety. On Rn or Cn, the closed sets of the Zariski topology are the solution sets of systems of polynomial equations.
A linear graph has a natural topology that generalises many of the geometric aspects of graphs with vertices and edges.
The Sierpiński space is the simplest non-discrete topological space. It has important relations to the theory of computation and semantics.
There exist numerous topologies on any given finite set. Such spaces are called finite topological spaces. Finite spaces are sometimes used to provide examples or counterexamples to conjectures about topological spaces in general.
Any set can be given the cofinite topology in which the open sets are the empty set and the sets whose complement is finite. This is the smallest T1 topology on any infinite set.
Any set can be given the cocountable topology, in which a set is defined as open if it is either empty or its complement is countable. When the set is uncountable, this topology serves as a counterexample in many situations.
The real line can also be given the lower limit topology. Here, the basic open sets are the half open intervals [a, b). This topology on R is strictly finer than the Euclidean topology defined above; a sequence converges to a point in this topology if and only if it converges from above in the Euclidean topology. This example shows that a set may have many distinct topologies defined on it.
If Γ is an ordinal number, then the set Γ = [0, Γ) may be endowed with the order topology generated by the intervals (a, b), [0, b) and (a, Γ) where a and b are elements of Γ.
Topological constructions
Every subset of a topological space can be given the subspace topology in which the open sets are the intersections of the open sets of the larger space with the subset. For any indexed family of topological spaces, the product can be given the product topology, which is generated by the inverse images of open sets of the factors under the projection mappings. For example, in finite products, a basis for the product topology consists of all products of open sets. For infinite products, there is the additional requirement that in a basic open set, all but finitely many of its projections are the entire space.
A quotient space is defined as follows: if X is a topological space and Y is a set, and if f : X → Y is a surjective function, then the quotient topology on Y is the collection of subsets of Y that have open inverse images under f. In other words, the quotient topology is the finest topology on Y for which f is continuous. A common example of a quotient topology is when an equivalence relation is defined on the topological space X. The map f is then the natural projection onto the set of equivalence classes.
The Vietoris topology on the set of all non-empty subsets of a topological space X, named for Leopold Vietoris, is generated by the following basis: for every n-tuple U1, ..., Un of open sets in X, we construct a basis set consisting of all subsets of the union of the Ui that have non-empty intersections with each Ui.
Classification of topological spaces
Topological spaces can be broadly classified, up to homeomorphism, by their topological properties. A topological property is a property of spaces that is invariant under homeomorphisms. To prove that two spaces are not homeomorphic it is sufficient to find a topological property not shared by them. Examples of such properties include connectedness, compactness, and various separation axioms.
See the article on topological properties for more details and examples.
Topological spaces with algebraic structure
For any algebraic objects we can introduce the discrete topology, under which the algebraic operations are continuous functions. For any such structure that is not finite, we often have a natural topology compatible with the algebraic operations, in the sense that the algebraic operations are still continuous. This leads to concepts such as topological groups, topological vector spaces, topological rings and local fields.
Topological spaces with order structure
- Spectral. A space is spectral if and only if it is the prime spectrum of a ring (Hochster theorem).
- Specialization preorder. In a space the specialization (or canonical) preorder is defined by x ≤ y if and only if cl{x} ⊆ cl{y}.
Specializations and generalizations
The following spaces and algebras are either more specialized or more general than the topological spaces discussed above.
- Proximity spaces provide a notion of closeness of two sets.
- Metric spaces embody a metric, a precise notion of distance between points.
- Uniform spaces axiomatize ordering the distance between distinct points.
- Cauchy spaces axiomatize the ability to test whether a net is Cauchy. Cauchy spaces provide a general setting for studying completions.
- Convergence spaces capture some of the features of convergence of filters.
- Grothendieck sites are categories with additional data axiomatizing whether a family of arrows covers an object. Sites are a general setting for defining sheaves.
See also
- Kolmogorov space (T0)
- accessible/Fréchet space (T1)
- Hausdorff space (T2)
- completely Hausdorff space and Urysohn space (T2½)
- regular space and regular Hausdorff space (T3)
- Tychonoff space and completely regular space (T3½)
- normal Hausdorff space (T4)
- completely normal Hausdorff space (T5)
- perfectly normal Hausdorff space (T6)
- Space (mathematics)
- Complete Heyting algebra – The system of all open sets of a given topological space ordered by inclusion is a complete Heyting algebra.
Notes
- ^ Armstrong 1983, definition 2.1.
- ^ Armstrong 1983, theorem 2.6.
References
- Armstrong, M. A. (1983) [1979]. Basic Topology. Undergraduate texts in mathematics. Springer. ISBN 0-387-90839-0.
- Bredon, Glen E., Topology and Geometry (Graduate Texts in Mathematics), Springer; 1st edition (October 17, 1997). ISBN 0-387-97926-3.
- Bourbaki, Nicolas; Elements of Mathematics: General Topology, Addison-Wesley (1966).
- Čech, Eduard; Point Sets, Academic Press (1969).
- Fulton, William, Algebraic Topology, (Graduate Texts in Mathematics), Springer; 1st edition (September 5, 1997). ISBN 0-387-94327-7.
- Lipschutz, Seymour; Schaum's Outline of General Topology, McGraw-Hill; 1st edition (June 1, 1968). ISBN 0-07-037988-2.
- Munkres, James; Topology, Prentice Hall; 2nd edition (December 28, 1999). ISBN 0-13-181629-2.
- Runde, Volker; A Taste of Topology (Universitext), Springer; 1st edition (July 6, 2005). ISBN 0-387-25790-X.
- Steen, Lynn A. and Seebach, J. Arthur Jr.; Counterexamples in Topology, Holt, Rinehart and Winston (1970). ISBN 0-03-079485-4.
- Willard, Stephen (2004). General Topology. Dover Publications. ISBN 0-486-43479-6.